Advertisement
Grab your lab coat. Let's get started
Welcome!
Welcome!
Create an account below to get 6 C&EN articles per month, receive newsletters and more - all free.
It seems this is your first time logging in online. Please enter the following information to continue.
As an ACS member you automatically get access to this site. All we need is few more details to create your reading experience.
Not you? Sign in with a different account.
Not you? Sign in with a different account.
ERROR 1
ERROR 1
ERROR 2
ERROR 2
ERROR 2
ERROR 2
ERROR 2
Password and Confirm password must match.
If you have an ACS member number, please enter it here so we can link this account to your membership. (optional)
ERROR 2
ACS values your privacy. By submitting your information, you are gaining access to C&EN and subscribing to our weekly newsletter. We use the information you provide to make your reading experience better, and we will never sell your data to third party members.
Environment
Borane Compound Turns Off When Sensing Cyanide
A fluorescing sulfonium borane compound can sense the presence of cyanide ions in water at concentrations less than 1 ppm
by Jyllian N. Kemsley
June 15, 2009
| A version of this story appeared in
Volume 87, Issue 24

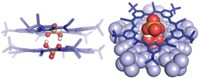
A sulfonium borane compound can sense the presence of cyanide ions in water at concentrations less than 1 ppm, an important development for efforts to test drinking water for the poison, reports a group led by François P. Gabbaï of Texas A&M University (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., DOI: 10.1002/anie.200901275). The compound contains adjacent sulfonium and dimesitylboryl moieties connected by an o-phenylene linker. The trigonal planar boron center is coordinatively unsaturated and mediates the π-conjugation of its aromatic ligands, resulting in a fluorescent blue chromophore. When CN- is present in solution, it latches onto the boron and quenches the fluorescence. Structural analysis of the B-CN adduct reveals that the sulfonium group stabilizes cyanide through donor-acceptor and Coulombic interactions. The researchers found that the compound's fluorescence is almost completely quenched within an hour for 200 ppb CN, the maximum contaminant level for drinking water set by EPA, and 33% quenched after an hour for 50 ppb CN-, the maximum contaminant level for drinking water in the European Union. The sulfonium borane "is one of the rare molecular systems competent for cyanide sensing at the sub-parts-per-million level in water," the researchers write.



Join the conversation
Contact the reporter
Submit a Letter to the Editor for publication
Engage with us on Twitter