Advertisement
Grab your lab coat. Let's get started
Welcome!
Welcome!
Create an account below to get 6 C&EN articles per month, receive newsletters and more - all free.
It seems this is your first time logging in online. Please enter the following information to continue.
As an ACS member you automatically get access to this site. All we need is few more details to create your reading experience.
Not you? Sign in with a different account.
Not you? Sign in with a different account.
ERROR 1
ERROR 1
ERROR 2
ERROR 2
ERROR 2
ERROR 2
ERROR 2
Password and Confirm password must match.
If you have an ACS member number, please enter it here so we can link this account to your membership. (optional)
ERROR 2
ACS values your privacy. By submitting your information, you are gaining access to C&EN and subscribing to our weekly newsletter. We use the information you provide to make your reading experience better, and we will never sell your data to third party members.
Materials
Biomimetic And Extreme Surface-Area Frameworks
MOFs with enzymelike catalytic properties and record-setting surface areas debuted in separate studies
by Mitch Jacoby
September 3, 2012
| A version of this story appeared in
Volume 90, Issue 36
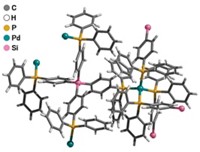
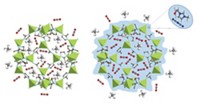
Two developments in the area of metal-organic framework (MOF) compounds may broaden commercialization and range of application of this class of porous crystals, which are composed of metal clusters joined by organic linkers. In one study, a team led by Texas A&M University chemists Zhi-Yuan Gu, Dawei Feng, and Hong-Cai Zhou used hemelike Fe-carboxyphenyl porphyrin units, which resemble enzyme cofactors, to link Zr6 clusters, forming a large-channel (3.7-nm diameter) MOF with exceptional stability in aqueous media. The team used the enzyme mimic to catalyze oxidation of pyrogallol and other common test compounds with hydrogen peroxide and measured high levels of catalytic activity and chemical selectivity (Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., DOI: 10.1002/anie.201204475). In the other study, researchers including Northwestern University’s Omar K. Farha and Joseph T. Hupp have synthesized two new MOFs from copper clusters and paddle-wheel-shaped carboxylate linkers that exhibit record-setting surface areas of just over 7,000 m2 per gram, as measured by a standard gas-uptake method. The high surface areas, which are crucial for gas storage applications, surpass the recent record—6,000 m2/g (J. Am. Chem. Soc., DOI: 10.1021/ja3055639). The team showed computationally that by tailoring the organic ligands, MOFs can reach surface areas as high as 14,600 m2/g.


Join the conversation
Contact the reporter
Submit a Letter to the Editor for publication
Engage with us on Twitter