Advertisement
Grab your lab coat. Let's get started
Welcome!
Welcome!
Create an account below to get 6 C&EN articles per month, receive newsletters and more - all free.
It seems this is your first time logging in online. Please enter the following information to continue.
As an ACS member you automatically get access to this site. All we need is few more details to create your reading experience.
Not you? Sign in with a different account.
Not you? Sign in with a different account.
ERROR 1
ERROR 1
ERROR 2
ERROR 2
ERROR 2
ERROR 2
ERROR 2
Password and Confirm password must match.
If you have an ACS member number, please enter it here so we can link this account to your membership. (optional)
ERROR 2
ACS values your privacy. By submitting your information, you are gaining access to C&EN and subscribing to our weekly newsletter. We use the information you provide to make your reading experience better, and we will never sell your data to third party members.
Oncology
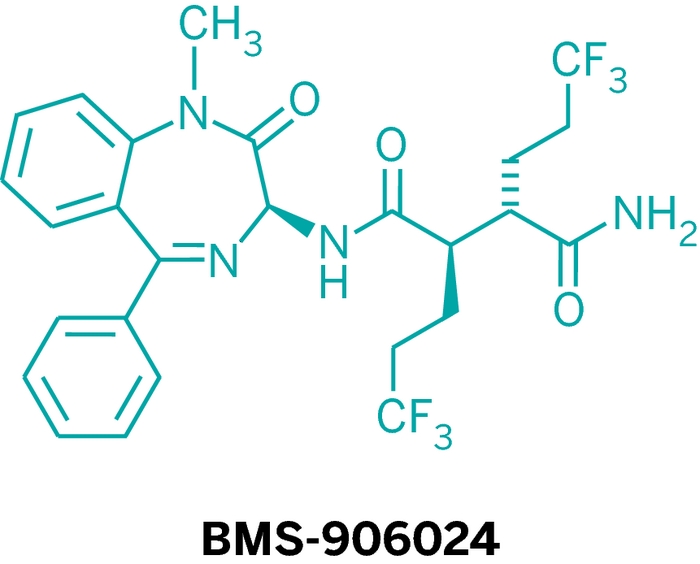
BMS-906024, Notch Signaling Inhibitor
by Carmen Drahl
April 22, 2013
| A version of this story appeared in
Volume 91, Issue 16

For some disease targets, an indirect approach may be best. Or so Ashvinikumar V. Gavai and his colleagues at Bristol-Myers Squibb found in their quest toward a potential cancer drug. Gavai unveiled BMS-906024, which is an experimental—and slightly roundabout—treatment for a number of cancers, including breast, lung, and colon cancers, and leukemia.
COVER STORY
BMS-906024, Notch Signaling Inhibitor
Cancers have a tendency to relapse or to become resistant to treatments that once worked. Research at BMS and elsewhere had suggested that a family of proteins called Notch is implicated in that resistance and in cancer progression more generally. Gavai, director of oncology chemistry at BMS in Princeton, N.J., and his team set out to block Notch family signaling.
Notch family members lack enzymatic activity, so blocking them directly is difficult. Instead, BMS developed inhibitors of an enzyme that is essential for activating Notch signaling—γ-secretase.
BMS-906024
\
Company: Bristol-Myers Squibb
Target: pan-Notch
Disease: breast, lung, colon cancer; leukemia
Interfering with Notch, even in this indirect way, can have detrimental effects on the gastrointestinal tract. Only two of the four Notch family members are linked to that side effect, Gavai says. But he and his team think their drug will be most effective if it acts on all four family members roughly equally—a so-called pan-Notch inhibitor. By selecting a molecule that’s well tolerated in animals and carefully scheduling doses of the drug in humans, it could be possible to minimize side effects, he says.
The BMS team relied on Notch signaling assays in leukemia and breast cancer cell lines to find leads. They soon learned that for their molecules to work, three chiral centers had to be in the S,R,S configuration. After that, they strove to make the molecules last in the bloodstream. They removed an isobutyl group and tweaked some other parts of their candidate’s succinamide side chain. It was tough to retain both a long half-life and activity against Notch, Gavai told C&EN. “You’d optimize one and lose the other.”
His team threaded the needle with BMS-906024. Their studies with mice suggest that a dose of 4–6 mg once a week could be effective in people. That’s lower than doses being tested for other Notch-targeted agents, according to the website clinicaltrials.gov. The mouse studies also back the idea that Notch is involved in cancer drug resistance and suggest that Notch could be a target for taking on cancer stem cells, which are notoriously resistant to chemotherapy.
BMS-906024 is in Phase I clinical trials, both alone and in combination with other agents. Patients with colon, lung, breast, and other cancers are receiving intravenous doses of the compound to determine its safety and optimum dose ranges.


Join the conversation
Contact the reporter
Submit a Letter to the Editor for publication
Engage with us on Twitter