Advertisement
Grab your lab coat. Let's get started
Welcome!
Welcome!
Create an account below to get 6 C&EN articles per month, receive newsletters and more - all free.
It seems this is your first time logging in online. Please enter the following information to continue.
As an ACS member you automatically get access to this site. All we need is few more details to create your reading experience.
Not you? Sign in with a different account.
Not you? Sign in with a different account.
ERROR 1
ERROR 1
ERROR 2
ERROR 2
ERROR 2
ERROR 2
ERROR 2
Password and Confirm password must match.
If you have an ACS member number, please enter it here so we can link this account to your membership. (optional)
ERROR 2
ACS values your privacy. By submitting your information, you are gaining access to C&EN and subscribing to our weekly newsletter. We use the information you provide to make your reading experience better, and we will never sell your data to third party members.
Analytical Chemistry
Plant Analysis Made Simple
Mass Spectrometry: Researchers use a quick jolt of electricity to ionize samples directly from plant tissue
by Sarah Webb
October 11, 2011

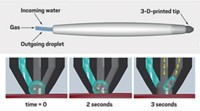
Analyzing the chemicals within a plant is now as easy as snipping a leaf and jolting it with electricity. Researchers report a method called leaf spray to quickly ionize chemicals within or on the surface of plants for analysis by mass spectrometry (Anal. Chem., DOI: 10.1021/ac2020273).

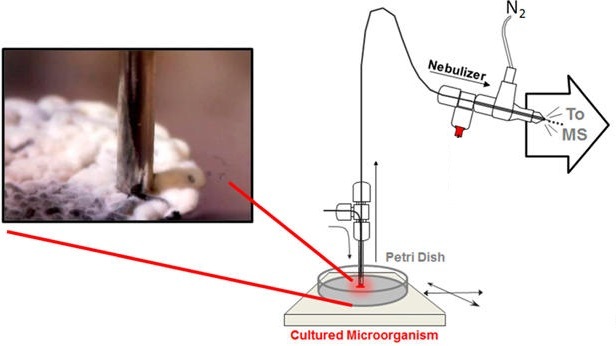
Zheng Ouyang, R. Graham Cooks, and their colleagues at Purdue University develop mass spectrometry techniques to study biological samples with little sample preparation. After the researchers devised a method that ionizes biological samples adsorbed onto wet paper, called paper spray, they realized they could adapt the technique to study plants, Ouyang says.
Both the paper and plant techniques rely on applying an electrical potential across a wet surface to produce a spray of ionized chemicals within tiny liquid droplets. In the plant technique, the scientists attach copper clips to the plant tissue, apply a 4.5 kV jolt to it, and aim the tissue’s spray of chemicals at the inlet valve of a mass spectrometer.
To obtain better quality data, the researchers sometimes make small cuts in the plant tissue to give it a point. But otherwise the method is non-invasive. Also the only solvent needed is an occasional spritzing of water.
The researchers used the technique to analyze leaves, roots, seeds, and fruits from several types of plants, including green onions, peanuts, and cranberries. The method even worked on living potato and tomato plants.
With the technique, Ouyang and his team could measure alkaloids, sugars, lipids, amino acids, and other compounds in the plant tissues. Sample preparation takes seconds, which could allow researchers to routinely measure rapid chemical changes within plants, such as responses to stress. Traditionally, such studies have involved time-consuming sample preparation including chromatography, Ouyang says. “We want to make it really simple.”


Join the conversation
Contact the reporter
Submit a Letter to the Editor for publication
Engage with us on Twitter