Advertisement
Grab your lab coat. Let's get started
Welcome!
Welcome!
Create an account below to get 6 C&EN articles per month, receive newsletters and more - all free.
It seems this is your first time logging in online. Please enter the following information to continue.
As an ACS member you automatically get access to this site. All we need is few more details to create your reading experience.
Not you? Sign in with a different account.
Not you? Sign in with a different account.
ERROR 1
ERROR 1
ERROR 2
ERROR 2
ERROR 2
ERROR 2
ERROR 2
Password and Confirm password must match.
If you have an ACS member number, please enter it here so we can link this account to your membership. (optional)
ERROR 2
ACS values your privacy. By submitting your information, you are gaining access to C&EN and subscribing to our weekly newsletter. We use the information you provide to make your reading experience better, and we will never sell your data to third party members.
Policy
Digital Briefs
New Software and Websites for the Chemical Enterprise
by Lauren K. Wolf
November 24, 2008
| A version of this story appeared in
Volume 86, Issue 47
Database
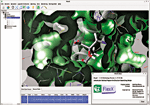
PSILO is a database system that provides a central repository for protein-drug-complex and macromolecule structural data and computational models. Crystallographers and computational modelers can use PSILO's Web-based interface to search and download structures from public sources, such as the Protein Data Bank (PDB), or to store proprietary structures. The software safeguards such proprietary data and allows collaborative edits to and annotation of in-house structures by multiple users. PSILO integrates into Web browser search bars and enables users to track favorite searches and hit lists. In addition, the system is capable of graphically comparing structure files, displaying electron densities for structures (shown), and illustrating active-site protein-ligand interactions. PSILO can be customized to work with nonstandard PDB files but requires users to already have either Oracle or MySQL database management programs installed. Chemical Computing Group, www.chemcomp.com
The Wiley Registry 8th Edition/NIST 2008 Mass Spectral Library, a combination of two trusted collections in mass spectrometry, was recently released by John Wiley & Sons. The updated database now features an electron ionization mass spec library with more than 560,000 spectra, a structure library with more than 348,000 searchable structures, and more than 2 million chemical names and synonyms. The complete NIST software suite—including MS Search, MS Interpreter v2.0, and AMDIS—comes with every Wiley registry/NIST 2008 library license. Users can search the collection for small-molecule organics, pharmaceuticals, illegal drugs, poisons, steroids, chemical warfare agents, and environmental pollutants. The database software is compatible with instruments manufactured by most mass spec instrumentation companies, including Agilent, Bruker, JEOL, Leco, PerkinElmer, ThermoFisher Scientific, Varian, and Waters. John Wiley & Sons, www.wiley.com/go/databases
Software
ActivityBase v7.2 is a drug discovery data management system that can be used by scientists to capture, analyze, and store experimental data from high-throughput screening, secondary screening, or compound profiling and complex in vitro assays. The software can be used in conjunction with plate-based and non-plate-based assays, including RNAi assays, ELISA, TaqMan assays, and MS/HPLC. Users can process data collected from a few plates to hundreds of plates, which can generate hundreds of thousands of data points. ActivityBase allows visualization of data in two and three dimensions, enabling identification of trends in results and potential experimental errors. Chemists using the software can register, search for, and display chemical information with associated biological data. Advanced structure searching includes substructure, superstructure, exact match, and similarity, and an advanced stereochemistry representation system is also available. The ActivityBase suite is integrated with Microsoft Excel and now includes the Excel Designer, a user-friendly front-end tool for building and editing data analysis templates quickly. IDBS, www.idbs.com/ActivityBase
ARChem (Automated Retrosynthetic Chemistry) Route Designer is a new software tool that aids synthetic chemists in planning organic synthesis. The software employs reaction databases such as CrossFire and Accelrys' Methods of Organic Synthesis (MOS), starting material catalogs such as those from Aldrich and Lancaster, and optional user input to aid in viable synthetic route design. With chemical perception algorithms, ARChem identifies reaction cores and generalizes reaction rules to make a retrosynthetic "solution tree" for a user's target molecule. The tree can be navigated, and every step along the chosen route is illustrated with examples from the literature. ARChem's exhaustive analysis is controlled by algorithms and rules that prevent combinatorial explosion. In addition, users can adjust the search depth and scope by targeting and protecting bonds. ARChem has a Web-based user interface and can be integrated with electronic notebooks in the lab. SimBioSys, www.simbiosys.ca
Lauren K. Wolf writes Digital Briefs. Information about new or revised electronic products can be sent to d-briefs@acs.org.





Join the conversation
Contact the reporter
Submit a Letter to the Editor for publication
Engage with us on Twitter