Advertisement
Grab your lab coat. Let's get started
Welcome!
Welcome!
Create an account below to get 6 C&EN articles per month, receive newsletters and more - all free.
It seems this is your first time logging in online. Please enter the following information to continue.
As an ACS member you automatically get access to this site. All we need is few more details to create your reading experience.
Not you? Sign in with a different account.
Not you? Sign in with a different account.
ERROR 1
ERROR 1
ERROR 2
ERROR 2
ERROR 2
ERROR 2
ERROR 2
Password and Confirm password must match.
If you have an ACS member number, please enter it here so we can link this account to your membership. (optional)
ERROR 2
ACS values your privacy. By submitting your information, you are gaining access to C&EN and subscribing to our weekly newsletter. We use the information you provide to make your reading experience better, and we will never sell your data to third party members.
Materials
Powerful Threads
Kevlar-nanowire hybrid collects energy from gentle friction
by Carmen Drahl
February 18, 2008
| A version of this story appeared in
Volume 86, Issue 7

Amid last week's London Fashion Week hoopla came the announcement of a decidedly more utilitarian fiber—one that can harvest energy from friction or low-frequency vibration. These fibers could be woven into fabrics that scavenge energy from body movements such as footsteps, providing power on the go (Nature 2008, 451, 809).
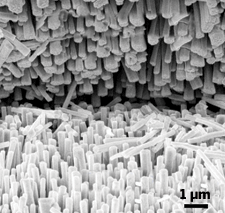
The practical threads, made by materials scientist Zhong L. Wang and colleagues at Georgia Tech, are flexible Kevlar fibers covered with zinc oxide (ZnO) nanowires. Wang's team entangled two of these fibers, which resemble tiny cylindrical brushes, and then applied gentle friction. Because ZnO is a semiconductor and has piezoelectric properties—it can generate a voltage in response to mechanical stress—the energy from the applied friction was converted to electricity.
Nanodevice expert Charles M. Lieber of Harvard University praises the "highly innovative materials chemistry" Wang's team employed to make Kevlar fibers that were still supple even after they were ensheathed in crystalline ZnO, calling it "a first." The key was to surround the fiber with a thin layer of seed ZnO crystals from which nanowires could sprout, Wang explains. "The thinner the seed crystal is, the more flexibility the fiber has." He emphasizes that the procedure is inexpensive and can be easily scaled up.
To generate electricity, the team wound together two ZnO nanowire-covered fibers, one of which they first coated with gold. Pulling the fibers using a tiny spring-loaded device makes the ZnO nanowires and their gold-coated counterparts grind together at the interfaces, like the gnashing of millions of microscopic teeth. The specialized junction between the gold metal and the ZnO semiconductor allows current to flow only in one direction, so that all of the currents add up constructively even as nanowires bend in different directions.
But just rubbing two fibers together doesn't generate enough power to be useful, Wang says. He now hopes to find an efficient way to weave fibers together that maximizes the power that they can generate.



Join the conversation
Contact the reporter
Submit a Letter to the Editor for publication
Engage with us on Twitter