Advertisement
Grab your lab coat. Let's get started
Welcome!
Welcome!
Create an account below to get 6 C&EN articles per month, receive newsletters and more - all free.
It seems this is your first time logging in online. Please enter the following information to continue.
As an ACS member you automatically get access to this site. All we need is few more details to create your reading experience.
Not you? Sign in with a different account.
Not you? Sign in with a different account.
ERROR 1
ERROR 1
ERROR 2
ERROR 2
ERROR 2
ERROR 2
ERROR 2
Password and Confirm password must match.
If you have an ACS member number, please enter it here so we can link this account to your membership. (optional)
ERROR 2
ACS values your privacy. By submitting your information, you are gaining access to C&EN and subscribing to our weekly newsletter. We use the information you provide to make your reading experience better, and we will never sell your data to third party members.
Biological Chemistry
Opioid Receptor Gang Of Four
Two teams raced to publish the structures of four membrane proteins that control pain and pleasure signaling in the body
by Lauren K. Wolf
December 24, 2012
| A version of this story appeared in
Volume 90, Issue 52

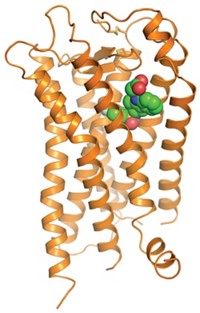
It’s been a big year for G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). Not only did the protein family garner the Nobel Prize in Chemistry (see above), but four of its members stepped into the spotlight. For the first time, researchers determined the X-ray crystal structures of opioid receptors, which are membrane proteins that mediate pain and pleasure in the body. In March, a friendly competition between two teams of scientists ended when Nature simultaneously published structures for the µ- and κ-opioid receptors (C&EN, March 26, page 11). One of the Nobel Laureates, Stanford University’s Brian K. Kobilka, teamed up with Stanford colleague Sébastien Granier and coworkers to crystalize a mouse µ-opioid receptor bound to the morphinelike inhibitor, β-funaltrexamine (DOI: 10.1038/nature10954). And a group led by Raymond C. Stevens of Scripps Research Institute characterized the human κ-receptor in a complex with an inhibitor called JDTic (DOI: 10.1038/nature10939). The two teams then raced to complete the gang of four opioid receptors, publishing structures for the remaining two in May (C&EN, May 21, page 32; Nature, DOI: 10.1038/nature11111 and 10.1038/nature11085). The Stanford team unveiled the details of a mouse δ-opioid receptor, and the Scripps team presented the finer points of the human nociceptin (orphanin FQ) receptor; as before, both proteins were bound to inhibitors. The researchers are now comparing the structures and binding pockets of the three classical opioid receptors—µ, κ, and δ—and the nonclassical receptor nociceptin. Knowledge of how each receptor binds its inhibitor could eventually lead to the design of better painkillers and antidepressants.



Join the conversation
Contact the reporter
Submit a Letter to the Editor for publication
Engage with us on Twitter