Advertisement
Grab your lab coat. Let's get started
Welcome!
Welcome!
Create an account below to get 6 C&EN articles per month, receive newsletters and more - all free.
It seems this is your first time logging in online. Please enter the following information to continue.
As an ACS member you automatically get access to this site. All we need is few more details to create your reading experience.
Not you? Sign in with a different account.
Not you? Sign in with a different account.
ERROR 1
ERROR 1
ERROR 2
ERROR 2
ERROR 2
ERROR 2
ERROR 2
Password and Confirm password must match.
If you have an ACS member number, please enter it here so we can link this account to your membership. (optional)
ERROR 2
ACS values your privacy. By submitting your information, you are gaining access to C&EN and subscribing to our weekly newsletter. We use the information you provide to make your reading experience better, and we will never sell your data to third party members.
Materials
Splashy route traps falling droplets in small capsules
Polymer-encased droplets could be used for reagent delivery or as small reactors
by Bethany Halford
February 15, 2018
| A version of this story appeared in
Volume 96, Issue 8


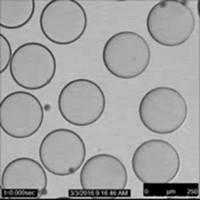
A new high-speed encapsulation method ensnares droplets in a thin polymer film. The technique, developed by Narayanan Menon, Deepak Kumar, and Thomas P. Russell of the University of Massachusetts, Amherst, along with Joseph D. Paulsen of Syracuse University, could create a new type of tiny chemical reaction flask or be used for targeted delivery of tiny amounts of liquid cargo.
In conventional liquid-encapsulation methods, a fluid layer of surfactants or particles forms a shell around the contents. The new technique involves dropping a hydrophobic liquid onto a solid, ultrathin polymer disk floating on an aqueous solution. The oil droplet’s impact pushes the disk, which is just 46–372 nm thick, down into the aqueous solution, coaxing the polymer to wrap around the oil and form a tiny bag—a process that takes less than half a second (Science 2018, DOI: 10.1126/science.aao1290). “All the droplet has to do is punch the polymer sheet through the liquid-air surface it is floating on,” Menon explains. After that, he says, surface tension does the work of encasing the droplet. The researchers also showed they could enclose droplets of water by dropping them into a hydrophobic liquid.
“There’s little chemical specificity involved in the basic process, so it allows one to overlay chemistry if somebody wants to go in that direction,” Menon, a physics professor, points out. “Now that the technique is out there, people with ingenuity should be able to add to it.” A clever chemist could add functionality to the polymer film to lead to a subsequent chemical reaction, for example.
Menon also notes that the whole process is reversible. “It’s a good thing for encapsulation but it’s also good for release,” he says. A bag holding oil will open in a hydrophobic environment, and a bag holding water will open in an aqueous solution.
Esther Amstad, an expert in encapsulation at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, Lausanne (EPFL), calls the new technique “elegant.” But, she says, “for this technology to become useful for applications, it must be scaled up, and this scale-up has not yet been done.”



Join the conversation
Contact the reporter
Submit a Letter to the Editor for publication
Engage with us on Twitter